Near Shore RTK Survey
October 1, 2024
Bayonet
Real-time kinematic (RTK) surveying has long been a cornerstone in high-precision positioning applications, especially in challenging coastal environments. RTK survey allows for centimeter-level accuracy by correcting signals from GNSS satellites in real-time, making it essential for coastal mapping, where accurate data is critical for navigation, engineering, and environmental studies. Recent advancements in the Bayonet Autonomous Underwater Ground Vehicles (AUGVs) have brought a new level of efficiency and precision to RTK coastal zone surveys.
First of all, what is RTK?
RTK positioning is a GPS correction technology that uses two receivers: a base station placed at a known location and a rover that collects data in real time. The base station provides real-time corrections to the rover, minimizing the signal errors caused by atmospheric conditions, satellite orbit, and clock discrepancies. In a coastal environment, where traditional methods of surveying are hampered by rough terrain and tidal fluctuations, RTK is essential for capturing accurate bathymetric and topographic data.
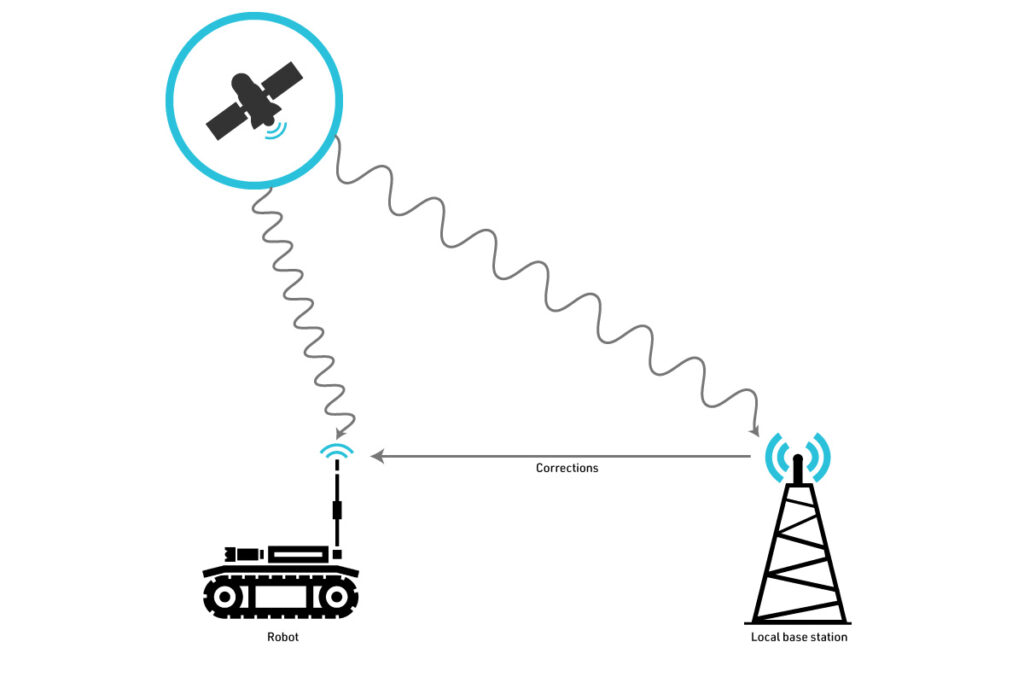
The challenge in coastal surveys, especially in the surf zone where land meets water, is the combination of shallow water, dynamic wave action, and difficult access for traditional survey vessels. This is where the Bayonet AUGV, equipped with RTK technology, becomes a game-changer.
Currently, beach and near shore surveys are performed in ways that heavily involves people, which is risky, or involves using highly specialized vehicles like the Coastal Research Amphibious Buggy (CRAB), which are expensive and in short supply.
The Bayonet AUGV: Designed for Coastal Missions
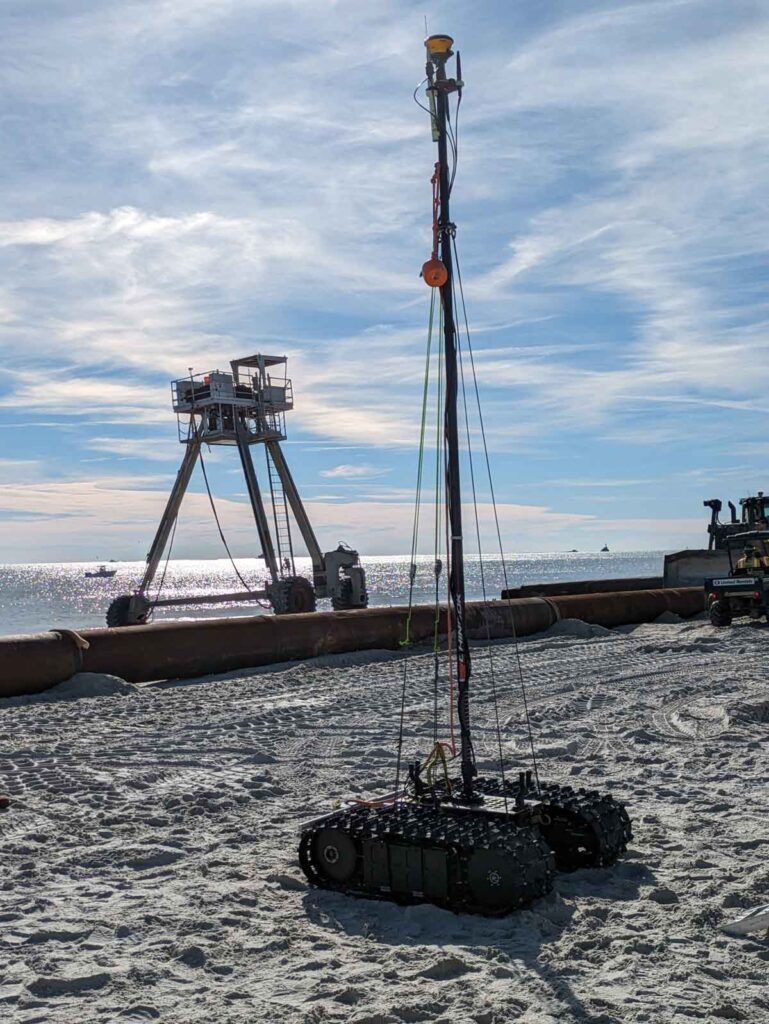
The Bayonet AUGV series, particularly the Bayonet 250 and 350 models, are autonomous robots specifically designed to operate in the surf and very nearshore zones, areas where conventional surface vehicles (boats or USVs) and subsurface vehicles (AUVs and ROVs) struggle to collect data. These robust robots can crawl along the seafloor, navigating the transition between land and water and can be custom equipped with a real-time kinematic (RTK) GNSS antenna mounted on a mast. This configuration allows the vehicle to capture high-resolution geospatial data, covering both bathymetry and topography seamlessly.
How It Works: A Technical Overview
The Bayonet AUGV operates with RTK positioning by integrating a GNSS antenna and real-time corrections from a nearby base station. As the AUGV moves through the surf zone, it continuously calculates its position using the GNSS data and adjusts its path accordingly. The vehicle’s IQNS processes this data in real time, enabling the robot to avoid obstacles and make decisions on the fly.
The RTK GNSS setup consists of a base station that sends correction signals to the Bayonet rover. This system significantly reduces the positional errors typically encountered in GNSS systems, which can range from several meters without corrections to less than a few centimeters with RTK. Additionally, the Bayonet’s sensors, including pressure sensors and fiber-optic gyros, provide supplementary data to further refine the vehicle’s positioning and orientation.
The ability of the Bayonet to crawl on the seafloor makes it ideal for areas where traditional vessels struggle, such as shallow waters with breaking waves or regions with complex underwater topographies like sandbars and rocky coastlines. This versatility makes it indispensable for coastal engineers and environmental scientists who need high-resolution data for coastal protection, erosion monitoring, or habitat mapping.

Real-World Applications and Benefits
Coastal surveys using the Bayonet AUGV provide data critical for a range of applications. Accurate bathymetry is essential for navigation, dredging operations, and coastal defense projects. Topographic data is invaluable for tracking shoreline changes, understanding sediment transport, and preparing for sea-level rise. By leveraging the precise data provided by the Bayonet’s RTK system, these tasks can be performed more efficiently and safely, with less human intervention.
The Bayonet series is designed to handle these tasks autonomously, meaning fewer personnel are required in potentially hazardous environments. Moreover, the integration of RTK technology allows for faster data collection with fewer errors, meaning that surveys can be completed more quickly and with greater confidence in the results.
Conclusion: The Future of Coastal Surveying
The combination of RTK surveying and autonomous underwater ground vehicles like the Bayonet AUGV represents a significant leap forward in coastal zone mapping. With their ability to operate in shallow, surf-zone environments and provide real-time, centimeter-accurate data, these vehicles are transforming how coastal surveys are conducted. The Bayonet’s successful tests at Greensea IQ’s facility demonstrate the robot’s potential to revolutionize coastal mapping, making it faster, safer, and more precise.
As the demand for accurate, real-time data continues to grow, particularly in the face of climate change and coastal development, the Bayonet AUGV’s role in providing this data will only become more critical.



